Author Archives: rcb
New Small Heterobifunctional Cross-linkers for Studying Protein-Protein interactions: Use of ESI-MS and STAVRO X 3.6.0.1 a Bioinformatics Software, Especially Suited for Identifying Intermolecular Crosslinking.
- April 16, 2018
- Science News@RCB
- rcb
- No Comments.
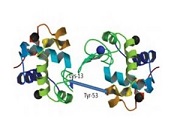
New small N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS)-aryl azide based heterobifunctional crosslinkers have been used as a ‘proof-of-concept’ to crosslink Lysozyme, in a two-step protocol, involving an initial incubation step followed by photolysis (366 nm, 6W lamp). This was further subjected to SDS-PAGE, excision of the ‘dimeric’ band, trypsin digestion and analyzed by ESI-MS and StavroX 3.6.0.1, a bioinformatics […]
Read moreParkinson’s disease associated α-synuclein oligomers causes cellular membrane damage and toxicity
- April 4, 2018
- Science News@RCB
- rcb
- 1 Comment.

α-Synuclein, a major constituent of proteinaceous inclusions named Lewy body, has been shown to be released and taken up by cells, which may facilitate its progressive pathological spreading and neuronal cell death in Parkinson’s disease. However, the pathophysiological effect and signalling cascade initiated by extracellular α-synuclein in cellular milieu are not well understood. Herein we […]
Read moreRole of Sporadic Parkinson Disease Associated Mutations A18T and A29S in Enhanced α-Synuclein Fibrillation and Cytotoxicity
- April 4, 2018
- Science News@RCB
- rcb
- 1 Comment.

Deposition of pre-synaptic protein α-synuclein in Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites in the substantia nigra region of brain has been linked with the clinical symptoms of the Parkinson’s disease (PD). Proteotoxic stress conditions and mutations that cause abnormal aggregation of α-synuclein have close association with onset of PD and its progression. Therefore, studies pertaining to […]
Read moreSPRY2 is a novel MET interactor that regulates metastatic potential and differentiation in rhabdomyosarcoma
- February 18, 2018
- Science News@RCB
- rcb
- No Comments.

Masum Saini, Aakanksha Verma and Sam J. Mathew Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a predominantly pediatric soft-tissue cancer where the tumor cells exhibit characteristics of the developing skeletal muscle, and the two most common sub-types are embryonal and alveolar RMS. Elevated activation of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) MET is frequent in RMS and is thought to […]
Read moreMechanism of formation of a toroid around DNA by the mismatch sensor protein
- January 8, 2018
- Science News@RCB
- rcb
- No Comments.

The DNA mismatch repair (MMR) pathway removes errors that appear during genome replication. MutS is the primary mismatch sensor and forms an asymmetric dimer that encircles DNA to bend it to scan for mismatches. The mechanism utilized to load DNA into the central tunnel was unknown and the origin of the force required to bend […]
Read more