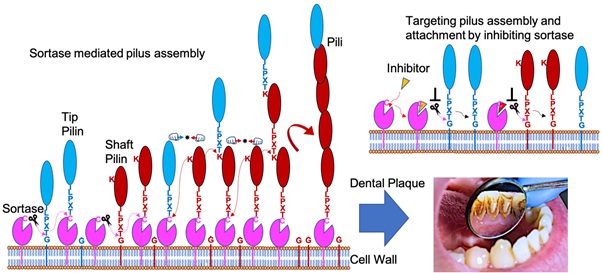
Oral biofilm or dental plaque is a yellowish sticky layer that grows on the tooth surface. It is a complex microbial biofilm community with over 700 different microbes and a major cause of multiple infections, including infective endocarditis. Its growth begins when certain bacteria called primary colonizers attach to oral tissues and undergo coaggregation. Primary […]
Read more