Monthly Archives: April 2018
Engulfment of Hb-activated platelets differentiates monocytes into pro-inflammatory macrophages in PNH patients.
- April 24, 2018
- Science News@RCB, Uncategorized
- rcb
- 2 Comments.
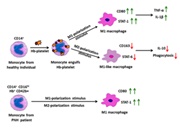
The distinct response shown by different phenotypes of macrophages and monocytes under various clinical conditions have put the heterogeneity of these cells into focus of investigation for several diseases. Recently we have described that after engulfing Hb-activated platelets, classical monocytes differentiated into pro-inflammatory phenotypes, which were abundant in the circulation of PNH and SCD patients. […]
Read moreAncestral Variations of the PCDHG Gene Cluster Predispose to Dyslexia in a Multiplex Family
- April 17, 2018
- Science News@RCB
- rcb
- No Comments.
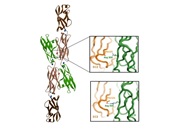
Dyslexia is a heritable neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by difficulties in reading and writing. In the present collaborative study, a strong correlation was observed between variations in the protocadherin gamma gene cluster and dyslexia in the members of one family.The protocadherins are trans synaptic molecules involved in cell-cell recognition in the human brain especially in the […]
Read moreDivided we conquer: The curious case of a bipartite bacterial effector
- April 17, 2018
- Science News@RCB
- rcb
- 6 Comments.
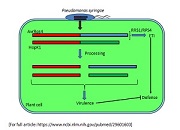
Plant-pathogen interactions are constant warfare where in most cases the counter-evolution of the latter is more rapid than the invaded plant-kind. This causes most biotechnological approaches including engineered transgenic plants to fail in their defense sustainability. Recent advances in understanding of functions of pathogenic effectors have greatly highlighted this phenomenon. The fundamental role of effectors […]
Read moreNitrene insertion into an adjacent o-methoxy group followed by nucleophilic addition to the heterocumulene intermediate: Experimental and computational studies
- April 16, 2018
- Science News@RCB
- rcb
- No Comments.
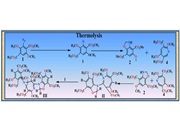
Aryl azides are considered as “green” reagents as most of their reactions involve only a benign loss of nitrogen. On the other hand, in the ‘Click’ reaction all the three nitrogen atoms are retained. Aryl azides are very reactive and many short lived intermediates are generated by both thermal and photochemical decomposition of aryl azides. […]
Read moreNew Small Heterobifunctional Cross-linkers for Studying Protein-Protein interactions: Use of ESI-MS and STAVRO X 3.6.0.1 a Bioinformatics Software, Especially Suited for Identifying Intermolecular Crosslinking.
- April 16, 2018
- Science News@RCB
- rcb
- No Comments.
New small N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS)-aryl azide based heterobifunctional crosslinkers have been used as a ‘proof-of-concept’ to crosslink Lysozyme, in a two-step protocol, involving an initial incubation step followed by photolysis (366 nm, 6W lamp). This was further subjected to SDS-PAGE, excision of the ‘dimeric’ band, trypsin digestion and analyzed by ESI-MS and StavroX 3.6.0.1, a bioinformatics […]
Read more